Crypto-Engine
Introduction to the usage of crypto-engine
Module Introduction
The crypto-engine implements hardware encryption algorithms to encrypt plaintext.
Function Introduction
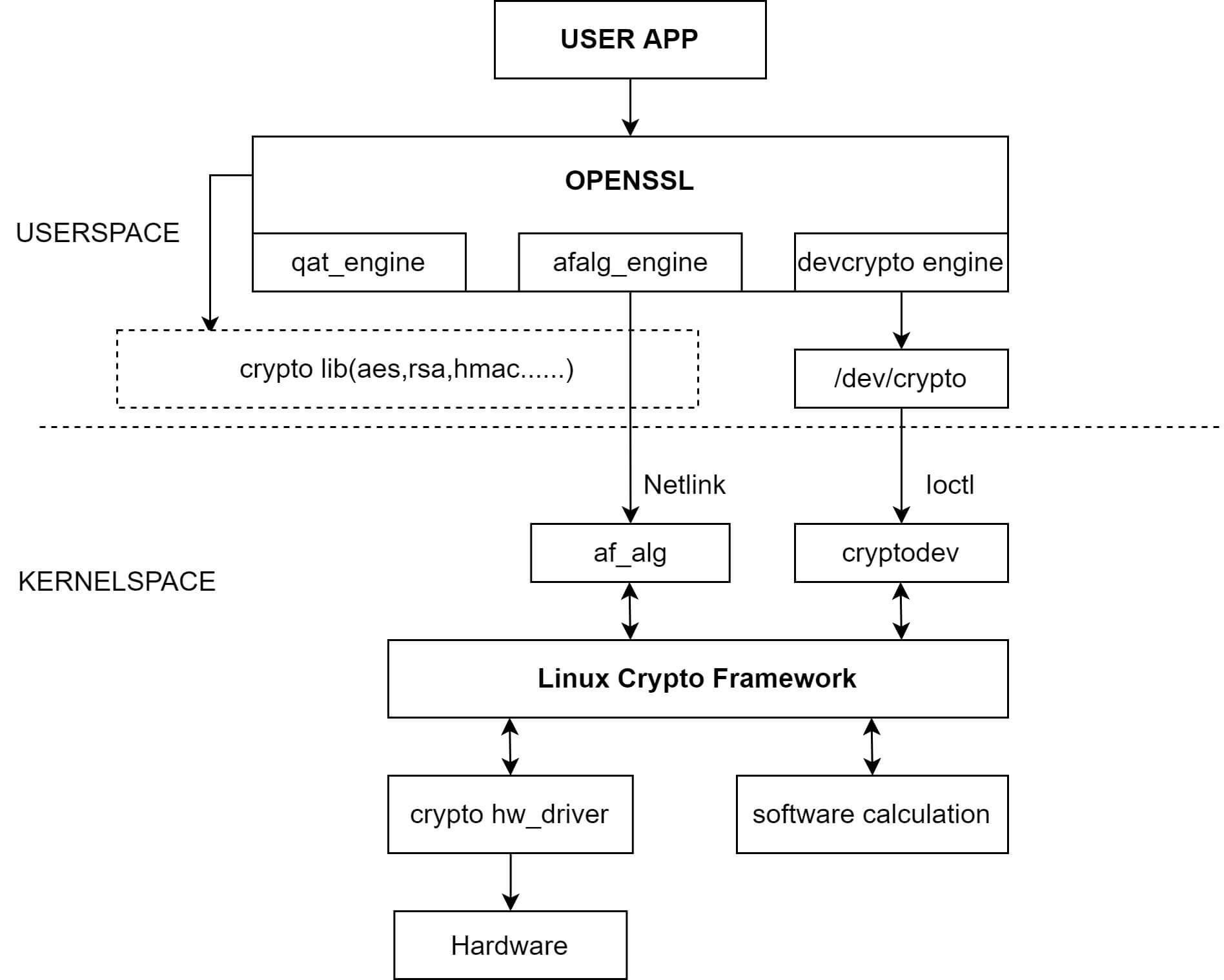 The k1 crypto-engine (also known as ce) implements (ecb/cbc/xts-)aes encryption algorithms in hardware.
The k1 crypto-engine (also known as ce) implements (ecb/cbc/xts-)aes encryption algorithms in hardware.
Source Code Structure Introduction
The ce driver code is under drivers/crypto/spacemit:
drivers/crypto/spacemit
|--spacemit_ce_engine.c # ce driver code
|--spacemit-ce-glue.c # encryption algorithms implemented based on ce driver
|--spacemit_engine.h
The kernel framework layer of crypto is implemented under the kernel crypto path, which is not detailed here.
Key Features
Features
Supports aes encryption algorithms in ecb/cbc/xts modes
Performance Parameters
Pure hardware performance can reach 500MB/s
The encryption process implemented by the kernel can reach 280MB/s (for data larger than 128k)
Testing Method:
openssl speed tool, the maximum data size supported by the openssl tool code is 16k, it can be developed again to change to 128k
openssl speed -elapsed -async_jobs 1 -engine afalg -evp aes-128-cbc -multi 1
Configuration Introduction
Mainly including driver enable configuration and dts configuration
CONFIG Configuration
CONFIG_CRYPTO This is provided for the kernel platform crypto framework, and should be Y under the support of k1 ce driver
CONFIG_CRYPTO=y
CONFIG_SPACEMIT_REE_AES=y
CONFIG_SPACEMIT_REE_ENGINE=y
dts Configuration
The ce has no input and output signals, just configure the clock reset resources in dts
dtsi Configuration Example
Configure the base address of the ce controller and the clock reset resources in dtsi, no need to change under normal circumstances
spacemit_crypto_engine@d8600000 {
compatible = "spacemit,crypto_engine";
spacemit-crypto-engine-0 = <0xd8600000 0x00100000>;
interrupt-parent = <&intc>;
interrupts = <113>;
num-engines = <1>;
clocks = <&ccu CLK_AES>;
resets = <&reset RESET_AES>;
interconnects = <&dram_range5>;
interconnect-names = "dma-mem";
status = "okay";
};
Interface Introduction
API Introduction
The AES driver mainly implements two APIs for encryption and decryption registered in the crypto framework Commonly used:
Taking cbc as an example
static int cbc_encrypt(struct skcipher_request *req)
This interface implements the hardware cbc mode encryption function of ce
static int cbc_decrypt(struct skcipher_request *req)
This interface implements the hardware cbc mode decryption function of ce
Testing Introduction
First, verify whether the aes algorithm is registered successfully
cat /proc/crypto
The result is as follows
name : xts(aes)
driver : __driver-xts-aes-spacemit-ce1
module : kernel
priority : 500
refcnt : 1
selftest : passed
internal : no
type : skcipher
async : yes
blocksize : 16
min keysize : 32
max keysize : 64
ivsize : 16
chunksize : 16
walksize : 16
name : cbc(aes)
driver : __driver-cbc-aes-spacemit-ce1
module : kernel
priority : 500
refcnt : 1
selftest : passed
internal : no
type : skcipher
async : yes
blocksize : 16
min keysize : 16
max keysize : 32
ivsize : 16
chunksize : 16
walksize : 16
name : ecb(aes)
driver : __driver-ecb-aes-spacemit-ce1
module : kernel
priority : 500
refcnt : 2
selftest : passed
internal : no
type : skcipher
async : yes
blocksize : 16
min keysize : 16
max keysize : 32
ivsize : 16
chunksize : 16
walksize : 16
The functionality of the encryption algorithm can be tested using the openssl tool, as follows:
echo "hello,world" | openssl enc -aes128 -e -a -salt -engine afalg //Encrypt string
echo "Automatically generated key for encryption" | openssl enc -engine afalg -aes128 -a -d -salt //Decrypt string
openssl enc -aes128 -e -engine afalg -in data.txt -out encrypt.txt -pass pass:12345678 //Encrypt using a key
openssl enc -aes-cbc -d -engine afalg -in encrypt.txt -out data.txt -pass pass:12345678 //Decrypt using a key
Compare the decrypted string/file with the original data before encryption, if they are the same, the encryption function is normal

