Machine Learning
The NXP eIQ Machine Learning Software Development Environment (hereinafter referred to as "NXP eIQ") provides a set of libraries and development tools for machine learning applications targeting NXP microcontrollers and application processors. The NXP eIQ is contained in the meta-imx/meta-ml Yocto layer. See also the i.MX Yocto Project User's Guide (IMXLXYOCTOUG) for more information. The following five inference engines are currently supported in the NXP eIQ software stack: TensorFlow Lite, ONNX Runtime, PyTorch, DeepView RT, and OpenCV. The following figure shows the supported eIQ inference engines across the computing units.
1、Software Stack Introduction
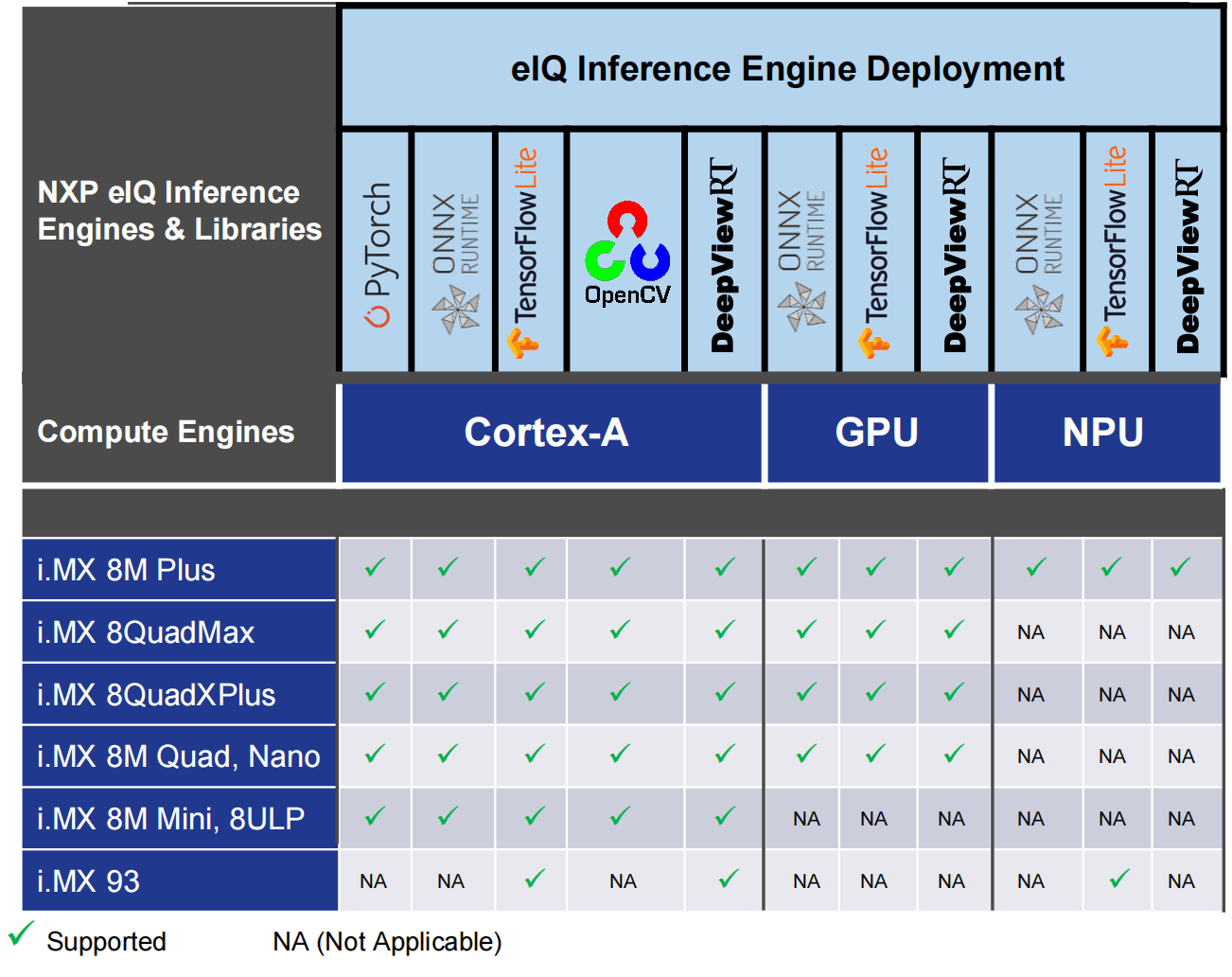
The NXP eIQ inference engines support multi-threaded execution on Cortex-A cores. Additionally, ONNX Runtime, TensorFlow Lite, and DeepViewRT also support acceleration on the GPU or NPU through Neural Network Runtime (NNRT). Generally, the NXP eIQ is prepared to support the following key application domains:
-
Vision
-
Multi camera observation
-
Active object recognition
-
Gesture control
-
-
Voice
- Voice processing
- Home entertainment
-
Sound
- Smart sense and control
- Visual inspection
- Sound monitoring
2、eIQ Inference Runtime Overview on i.MX 8 Series
The chapter describes an overview of the NXP eIQ software stack for use with the NXP Neural Network Accelerator IPs (GPU or NPU). The following figure shows the data flow between each element. The below diagram has two key parts:
- Neural Network Runtime (NNRT), which is a middleware bridging various inference frameworks and the NN accelerator driver.
- TIM-VX, which is a software integration module to facilitate deployment of Neural Networks on OpenVX enabled ML accelerators.
ModelRunner for DeepViewRT is a server application being able to receive requests using HTTP REST API, Python API, or UNIX RPC service, and delegate those to different inference engines, or the NN accelerator driver directly.
The NNRT supplies different backends for Android NN HAL, ONNX, and TensorFlow Lite allowing quick application deployment. The NNRT also empowers an application-oriented framework for use with i.MX8 processors. Application frameworks such as Android NN, and TensorFlow Lite can be speed-up by NNRT directly benefiting from its built-in backend plug-ins. Additional backend can be also implemented to expand support for other frameworks.
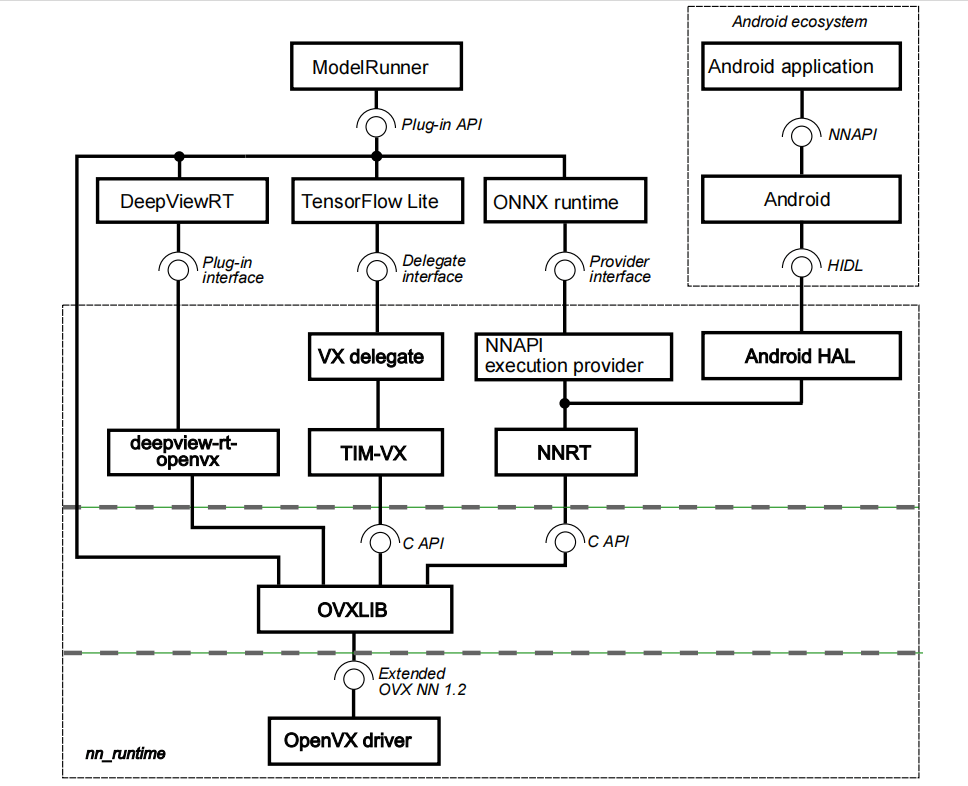
NNRT supports different Machine Learning frameworks by registering itself as a compute backend. Because each framework defines a different backend API, a lightweight backend layer is designed for each:
- For Android NN, the NNRT follows the Android HIDL definition. It is compatible with v1.2 HAL interface
In doing so, NNRT unifies application framework differences and provides an universal runtime interface into the driver stack. At the same time, NNRT also acts as the heterogeneous compute platform for further distributing workloads efficiently across i.MX8 compute devices, such as NPU, GPU and CPU.
Note: Both the OpenCV and PyTorch inference engines are currently not supported for running on the NXP NN accelerators. Therefore, both frameworks are not included in the above NXP-NN architecture diagram.

